Europe Hybrid Cars Market Report Summary
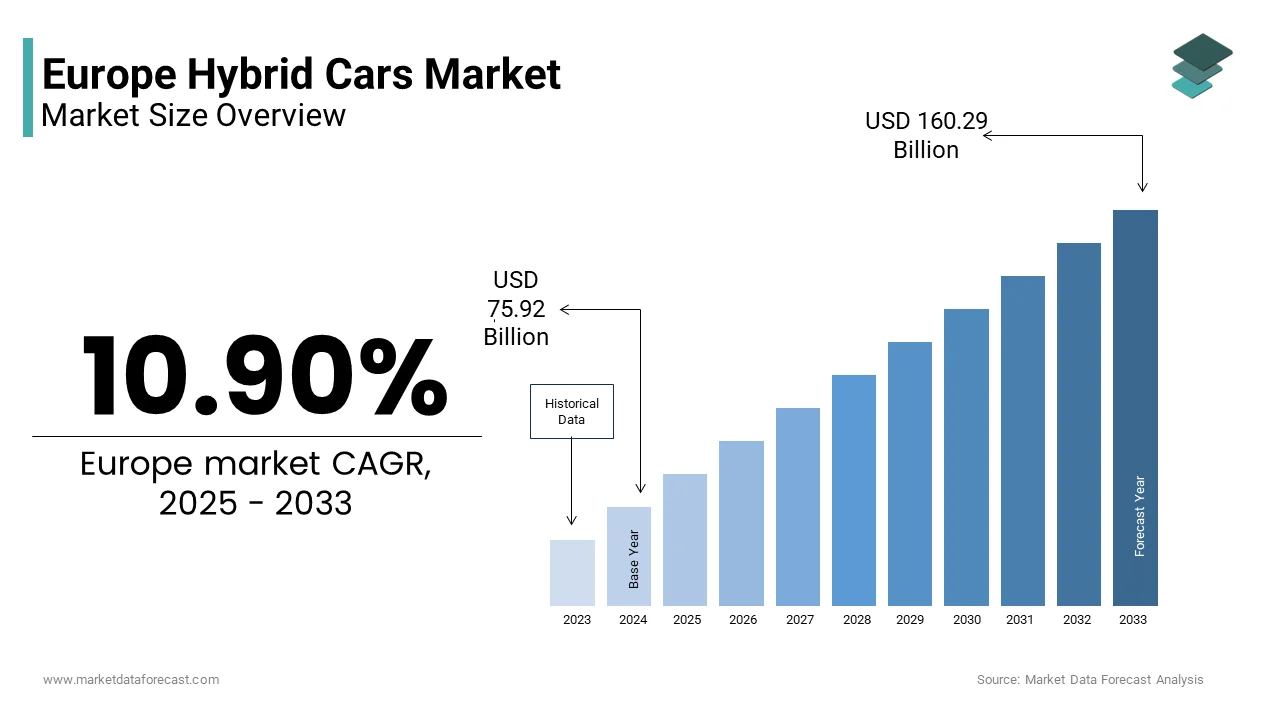
The Europe hybrid car market was valued at USD 68.45 billion in 2024, is estimated to reach USD 75.92 billion in 2025, and is projected to reach USD 160.29 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 10.90% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2033. Market growth is driven by stringent European emission regulations, rising fuel prices, expanding electrification strategies by automakers, and growing consumer preference for low-emission mobility solutions. Hybrid vehicles are increasingly viewed as a practical transition technology between conventional internal combustion engine vehicles and fully electric vehicles, especially in regions with uneven charging infrastructure.
Rising adoption of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), supportive government incentives, and increasing availability of hybrid models across multiple vehicle categories are further accelerating market expansion. Additionally, consumer demand for fuel-efficient SUVs with lower carbon footprints is reshaping product offerings across Europe.
Key Market Trends
Strong growth in plug-in hybrid vehicles (PHEVs) due to extended electric-only driving range and regulatory incentives.
Increasing dominance of hybrid SUVs, combining performance, efficiency, and practicality.
AAutomakersfocus on fleet electrification to meet EU CO₂ emission targets.
Rising consumer acceptance of hybrids as a cost-effective and flexible alternative to fully electric vehicles.
Integration of advanced powertrain technologies, regenerative braking, and connected vehicle systems.
Segmental Insights
Based on the degree of hybridization, the plug-in hybrid vehicles segment dominated the Europe hybrid cars market by accounting for 56.5% share in 2024, driven by tax benefits, lower emissions ratings, and suitability for urban commuting.
By vehicle type, the SUV segment led the market, holding 51.5% share in 2024, supported by consumer preference for versatile, family-oriented vehicles combined with improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
Regional Insights
The Europe hybrid car market shows strong momentum across major automotive economies.
Germany led the market by accounting for 23.5% share in 2024, driven by a strong automotive manufacturing base, fleet electrification mandates, and consumer incentives.
France emerged as the second-largest market, supported by aggressive emission reduction policies and electrified mobility programs.
The United Kingdom remains a key contributor, with hybrid vehicles forming a significant share of new electrified car registrations amid tightening emission norms.
Competitive Landscape
The Europe hybrid car market is characterized by intense competition among global automotive manufacturers focused on powertrain innovation, model diversification, and compliance with emission standards. Leading players are expanding hybrid portfolios across passenger cars and SUVs while investing in next-generation battery systems and software integration. Prominent companies operating in the Europe hybrid cars market include Toyota Motor Corporation, BMW AG, Volkswagen Group, Audi AG, Mercedes-AMG GmbH, Porsche, Honda, Kia Corporation, Lexus, and Tesla.
Europe Hybrid Cars Market Size
The Europe hybrid carmarket size was valued at USD 68.45 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 75.92 billion in 2025 toandSD 160.29 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 10.90% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2033.
Hybrid cars include vehicles powered by a combination of internal combustion engines and electric propulsion systems that operate in tandem to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce tailpipe emissions. These vehicles include both conventional hybrids and plug-in hybrids and are distinct from fully battery electric vehicles due to their dual energy source architecture. According to Eurostat, the European Union’s passenger‑car fleet exceeded 259 million registered vehicles at the end of 2023. Urban air quality remains a pressing concern, with many city dwellers exposed to particulate matter levels that exceed World Health Organization guidelines. Against this backdrop, hybrid vehicles have emerged as a transitional technology that aligns with Europe’s decarbonization imperatives while accommodating infrastructural and behavioral constraints that impede immediate full electrification. The European Commission’s Fit for 55 packages further intensify pressure on automakers to adopt cleaner drivetrains, reinforcing the strategic relevance of hybrid solutions across diverse national markets with varying charging readiness and consumer preferences.
MARKET DRIVERS Stringent Emission Regulations Accelerate Hybrid Adoption
The European Union’s aggressive regulatory stance on vehicular carbon dioxide emissions is a major factor driving the growth of the Europe hybrid cars market. Under Regulation (EU) 2019/631, manufacturers must achieve a fleet‑wide average target of 95 g CO₂ per km for new passenger cars. Non‑compliance incurs financial penalties applied per gram exceeded per vehicle. This financial disincentive has compelled automakers such as Stellantis and Volkswagen Group to rapidly expand hybrid offerings as a compliance buffer while scaling battery‑electric vehicle production. In 2023, plug‑in hybrids and full hybrids collectively accounted for a substantial share of new car registrations in the European Union. Germany, France, and Italy have witnessed particularly steep adoption curves driven partly by corporate fleet decarbonization mandates under the EU Green Public Procurement criteria. Additionally, the upcoming Euro 7 standards scheduled for 2025 will impose tighter limits on nitrogen oxides and particulate matter,r further marginalizing conventional internal combustion engines. Hybrid architectures enable manufacturers to meet these evolving benchmarks without sacrificing vehicle range or refueling convenience, which is a critical consideration in regions with underdeveloped charging ecosystems, ms such as parts of Eastern and Southern Europe.
Consumer Preference for Fuel Efficiency Amid Economic Volatility
Elevated fuel prices and cost‑of‑living pressures have intensified European consumers’ sensitivity to vehicle operating expenses, making hybrid cars an attractive economic proposition, which is further contributing to the expansion of the Europe hybrid cars market. Fuel prices were highly volatile between 2021 and 2023, increasing consumer focus on fuel economy and total cost of ownership. In this environment, hybrids deliver tangible savings with many full‑hybrid models showing materially lower fuel consumption than equivalent gasoline‑only models in real‑world use. This translates into meaningful annual fuel‑cost reductions for average drivers covering typical annual mileage. Countries such as Belgium and the Netherlands have observed a marked shift toward hybrid models in the compact and midsize segment,,s where total cost of ownership is a decisive purchase criterion. Furthermore, fiscal policies in nations like Portugal and Sweden offer reduced annual road taxes or other incentives for lower‑emission vehicles, indirectly favoring hybrids. For instance, a majority of prospective buyers prioritize fuel economy over some non‑essential features. This pragmatic shift underscores how macroeconomic headwinds are reshaping mobility preferences and reinforcing the value proposition of hybrid drivetrains across diverse income groups.
MARKET RESTRAINTS Insufficient Charging Infrastructure for Plug‑In Hybrids
Despite their electric capabilities, plug‑in hybrid electric vehicles require access to reliable and convenient charging facilities to realize their full environmental and economic benefits, which is hampering the growth of the Europe hybrid cars market. The European public charging network has expanded rapidly, but distribution remains uneven across member states. This geographic disparity undermines the utility of plug‑in hybrids in rural and peri‑urban areas where home charging is often unavailable due to multi‑unit dwellings or a lack of private parking. A significant share of European households lacks dedicated off‑street parking, which limits overnight charging potential. Consequently, many plug‑in hybrid owners operate their vehicles primarily in gasoline mode, de diminishing the intended emission reductions. Real‑world monitoring studies show that electric‑mode usage among many PHEV fleets is substantially lower than laboratory assumptions. This infrastructure deficit not only erodes consumer confidence but also weakens the policy rationale for treating plug‑in hybrids as equivalent to battery‑electric vehicles in national zero‑emission vehicle mandates. Without coordinated investment in ubiquitous and interoperable charging networks,rks the decarbonization potential of plug‑in hybrids will remain unrealized, particularly in Central and Eastern Europe.
Battery Raw‑Material Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
Hybrid vehicles rely on lithium, nickel, and cobalt‑based battery chemistries whose supply chains are increasingly exposed to geopolitical and environmental risks, which is further hindering the expansion of the Europe hybrid cars market. Global refining and processing capacity for key battery materials is concentrated in a small number of countries, creating strategic dependencies. The Democratic Republic of Congo supplies a major share of mined cobalt, which is raising concerns over ethical sourcing and supply continuity. Environmental and due‑diligence regulations within the European Union, including the forthcoming Battery Regulation, mandate stricter provenance checks, which increase compliance costs for automakers. Recycling and circular‑economy capacity for lithium‑ion batteries in Europe is still developing,g and current recovery rates for key materials remain limited. This low circularity rate heightens exposure to primary‑material market volatility, which has seen sharp price swings in recent years. Automakers have pursued long‑term offtake agreements and vertical integration to mitigate risk, but these measures do not fully insulate them from price spikes or logistical disruptions. Consequently, battery cost uncertainty impedes pricing stability for hybrids and complicates long‑term investment planning, ng especially as the industry explores next‑generation chemistries that are not yet proven at scale.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES Expansion Vehicle-to-Grid Integration Frameworks
The emergence of vehicle‑to‑grid technology provides a compelling opportunity for the Europe hybrid cars market. Although full hybrids lack plug‑in capability and therefore cannot feed power back to the grid, plug‑in hybrids equipped with bidirectional charging can serve as distributed energy assets. The European Union’s Clean Energy Package, adopted in 201,9 mandates that member states remove regulatory barriers to vehicle‑grid integration, which is enabling consumers to sell stored electricity during peak demand periods. Pilot projects in Denmark and the United Kingdom have demonstrated that individual plug‑in vehicles can generate meaningful grid service revenues in some schemes. With the European electricity grid projected to require substantial additional flexible capacity by 2030, this distributed resource could significantly enhance grid resilience. Furthermore, the European Commission’s Net Zero Industry Act prioritizes smart‑charging infrastructure deployment, which indirectly supports bidirectional capabilities. Countries like Italy and Spain are developing regulatory sandboxes to test vehicle‑to‑grid business models with incentives for early adopters. As renewable energy penetration grows, intermittent supply from wind and solar will necessitate responsive demand‑side resources, making plug‑in hybrids not merely transport tools but active participants in the energy transition. This dual functionality could reshape consumer valuation and accelerate market acceptance beyond traditional mobility metrics.
Growth of Circular Economy Initiatives in Automotive Manufacturing
Europe’s commitment to a circular economy offers a strategic opening for hybrid vehicle manufacturers to differentiate through sustainable production practices, which is another major opportunity in the Europe hybrid cars market. The EU Circular Economy Action Plan and related product‑policy workstreams are driving stronger requirements for durability, reparability, and recyclability in vehicle design. Hybrid systems with modular battery packs and standardized components align well with these objectives. Industry and alliance programs across Europe are piloting closed‑loop recycling processes for battery and power‑electronics materials, testing technologies to recover high shares of critical metals from end‑of‑life batteries. Companies like Volvo and Toyota have already integrated recycled materials into motor and component production, reducing reliance on virgin mining. Automotive recycling systems in Europe already recover the bulk of vehicle materials, and hybrid‑specific recycling processes can further increase recovery of high‑value battery and electronics streams. The European Commission’s forthcoming End‑of‑Life Vehicles and battery‑value‑chain rules will impose stricter material‑recovery targets and extended‑producer‑responsibility obligations, creating both compliance pressure and competitive advantage for early movers. Consumer sentiment is shifting toward sustainability and verified recycled content, strengthening market appeal for manufacturers that can credibly demonstrate circular practices. This convergence of regulatory policy, industrial innovation, and public expectation positions hybrid manufacturers to lead in sustainable mobility narratives while mitigating long‑term resource‑scarcity risks.
MARKET CHALLENGES Residual Value Uncertainty Due to Rapid Technological Obsolescence
Hybrid vehicles in Europe face significant depreciation risks stemming from the accelerating pace of powertrain innovation and policy shifts, which is a significant challenge to the growth of the Europe hybrid cars market. As governments advance zero‑emission vehicle mandates and urban low‑emission zones proliferate, the perceived longevity of hybrid technology is declining among consumers and fleet managers. Market data and dealer reports show that resale values for some hybrid models have weakened relative to both conventional and fully electric alternatives in recent years. This gap reflects market skepticism about the long‑term relevance of hybrid drivetrains, particularly in cities where access restrictions for higher‑emission vehicles are already in force or planned. The European Commission’s long‑term decarbonization proposals further compound this uncertainty as future clean‑vehicle definitions evolve. Leasing companies have responded by shortening contract durations for hybrids to mitigate residual‑value exposure. This dynamic discourages private buyers who prioritize asset retention and reduces fleet adoption where total cost‑of‑ownership calculations are highly sensitive to depreciation. Without standardized second‑life applications for hybrid batteries or policy clarity on their transitional role, the market risks a premature erosion of consumer confidence, which could stifle near‑term growth even as manufacturers invest in next‑generation hybrid architectures.
Fragmented National Incentive Structures Across Member States
The Europe hybrid‑car market operates within a disjointed policy landscape where national incentives for plug‑in hybrids vary dramatically in structure, eligibility, and duration. Some countries continue to offer purchase bonuses or tax advantages for low‑emission vehicles, while others have scaled back or restructured incentives, producing uneven market signals. This inconsistency complicates pan‑European marketing strategies and distorts cross‑border vehicle flows. Policy and tax disparities contribute materially to variation in hybrid ownership costs across the EU. Furthermore, some regions impose additional registration fees or weight‑based surcharges that disproportionately affect hybrids due to their dual‑powertrain mass. The absence of a harmonized EU framework undermines economies of scale for automakers and creates consumer confusion, particularly in cross‑border labor markets. As the European Commission advances industrial and Green Deal policy initiatives, calls for greater policy convergence have intensified, but sovereignty concerns limit rapid alignment. Until incentives reflect a unified decarbonization logic rather than divergent national fiscal priorities, the hybrid market will remain susceptible to abrupt demand shifts and suboptimal fleet‑turnover patterns.
REPORT COVERAGE
REPORT METRIC
DETAILS
Market Size Available
2024 to 2033
Base Year
2024
Forecast Period
2025 to 2033
CAGR
10.90%
Segments Covered
By Degree of Distribution, Vehicle Type, and Region.
Various Analyses Covered
Global, Regional, and Country-Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities
Regions Covered
UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic, and the Rest of Europe
Market Leaders Profiled
TOYOTA MOTOR CORPORATION, Lexus, Honda, BMW AG, Tesla, Volkswagen Group, Chevrolet, AUDI AG, Mercedes-AMG GmbH, Porsche, Kia Corporation
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS By Degree of Hybridization Insights
The plug‑in hybrid vehicles segment accounted for 56.5% of the Europe hybrid car market share in 2024. Full hybrids represent the remaining portion with slower growth momentum. The dominance of the plug‑in hybrid vehicles segment in this European market is primarily due to their eligibility for national purchase incentives, stricter urban access regulations, and superior electric‑only range compared to full hybrids. In markets like France and the Netherlands, government subsidies explicitly favor vehicles capable of grid connection, reinforcing consumer preference for plug‑in architectures. Additionally, automakers have prioritized plug‑in hybrid variants in premium and midsize segments where customers are more receptive to electrified options and willing to install home charging facilities. European cities are increasingly implementing low andzero-emissionn zones that restrict access for conventional vehicles but grant preferential access to low‑emission and plug‑in vehicles under current regulatory definitions. Hundreds of European cities now operate low‑emission zones, and major urban centers require vehicles to meet stringent Euro standards and low CO₂/NOx thresholds for unrestricted access. Plug‑in hybrids typically achieve much lower tailpipe CO₂ in electric‑first use than conventional powertrains, enabling compliance where some full hybrids running primarily on combustion may not. This policy‑driven advantage has reshaped fleet procurement strategies and municipal procurement rules under Green Public Procurement criteria, which further mandate minimum shares of low‑emission vehicles, accelerating institutional adoption. Consequently, urban regulatory design has become a structural tailwind for plug‑in hybrids, reinforcing their market leadership beyond mere consumer preference.
By Vehicle Insights
The SUV segment dominated the market by occupying 51.5% of the Europe hybrid cars market share in 2024. SUVs account for roughly half of new car registrations in recent years and dominate the Europe hybrid cars market by vehicle type. Hatchbacks and sedans make up the remainder. The dominating position of the UV segment is majorly fuelled by consumer demand for higher seating positions, versatile cargo space, and perceived safety advantages. Automakers have responded by launching hybrid variants across all SUV size classes from compact to large premium models. European buyers increasingly favor SUVs for their commanding road view, interior versatility, and all‑weather capability. Hybrid powertrains mitigate traditional fuel‑economy drawbacks of SUVs and improve urban drivability through electric torque and regenerative braking, further boosting desirability among families and fleet buyers.
COUNTRY ANALYSIS Germany Hybrid Cars Market
Germany held the leading position in the Europe hybrid cars market in 2024 by accounting for 23.5% of the regional market share. Germany serves as both a manufacturing powerhouse and a sophisticated consumer market with strong policy support for electrification. Domestic automakers such as BMW, Mercedes‑Benz, and Volkswagen offer extensive hybrid and plug‑in hybrid lineups across passenger and premium segments. Hybrid registrations showed year‑on‑year growth in 2023, and corporate fleets remain an important channel for hybrid uptake. Germany’s dense public charging network and urban low‑emission zones continue to support plug‑in usability and city access for low‑emission hybrids.
France Hybrid Cars Market
France captured the second biggest share of the Europe hybrid cars market in 2024. The growth of France in the European market is supported by policy incentives and strong domestic production from Stellantis and Renault. The government’s bonus‑malus framework and charging‑deployment programs encourage low‑emission vehicle adoption, and corporate fleets and urban circulation rules favor hybrids that meet low‑emission criteria. French consumers show strong interest in compact hybrid SUVs that suit urban driving and narrow streets. Domestic manufacturing and targeted incentives sustain France’s prominent role in the regional hybrid transition.
United Kingdom Hybrid Cars Market
The United Kingdom is a major regional market in Europe where hybrids form a significant share of electrified new‑car registrations. UK decarbonization policy and company‑car tax treatment have materially influenced plug‑in hybrid uptake, and fleet demand remains a key driver. The UK market also features a mature used‑hybrid segment and widespread adoption of digital fleet‑management and scheduling tools that support hybrid deployment. London’s low‑emission measures and national incentives continue to shape urban and corporate hybrid demand.
Italy Hybrid Cars Market
Italy is an important hybrid market. The purchase incentives, urban charging constraints, and strong consumer preference for fuel efficiency are fuelling the hybrid cars market expansion in Italy. National incentive schemes and regional policies support hybrid adoption, while limited home‑charging access in dense urban areas sustains demand for full hybrids that do not require plug‑in infrastructure. Fleet and municipal circulation rules further encourage low‑emission vehicle choices, and Italy’s mix of compact vehicle preferences keeps hybrids relevant across city and suburban segments.
Netherlands Hybrid Cars Market
The Netherlands is a leading adopter of plug‑in hybrids within Europe, shaped by historically favorable fiscal treatment for low‑emission company cars and a dense public charging network. Company‑car dynamics and urban environmental zones have driven high plug‑in hybrid penetration in the corporate segment, while a well‑developed second‑hand market supports residual values. Recent policy shifts are rebalancing incentives toward full electrification, but the Netherlands’ installed base, charging density,y and fleet orientation keep it a bellwether for plug‑in hybrid adoption.
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
Competition in the Europe hybrid cars market is intense and multifaceted, ed driven by technological differentiation, regulatory compliance,ce and consumer value propositions. Established automakers leverage scale, brand loyalty, and extensive dealer networks to maintain relevance, while newer entrants focus on niche segments or digital ownership experiences. The rivalry centers on electric range efficiency,y drivabili, ty, and total cost of ownership rather than price alone. Manufacturers continuously refine hybrid architectures to meet tightening CO2 standards and urban access rules, creating a dynamic innovation race. Corporate fleet channels represent a critical battleground with tailored leasing programs and tax-optimized models. Simultaneously, sustainability credentials, ls including battery sourcing and end-of-life recyclability, are increasingly influencing purchasing decisions. This layered competitive environment demandsagilityt, strategic foresight, and deep integration with Europe’s evolving energy and mobility ecosystem to sustlong-termterm market positioning amid rapid technological and policy shifts.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS TOYOTA MOTOR CORPORATION Lexus Honda Stellantis N.V. BMW AG Tesla Volkswagen Group Chevrolet AUDI AG Mercedes-AMG GmbH Porsche Kia Corporation Top Players In The Market Toyota maintains a strong presence in the Europe hybrid cars market through its long-standing leadership in full hybrid technology. The company introduced the Prius in Europe over two decades ago and has since expanded its hybrid lineup to include models like the Corolla, RAV4, and Yaris Cross. Toyota continues to invest in localized production with hybrid assembly lines in France and the United Kingdom. In 202,4 the company launched the next-generation Yaris Hybrid, featuring improved fuel efficiency and a more responsive electric motor. Toyota also collaborates with European cities promote low-emission mobility and supports recycling initiatives for hybrid batteries, aligning with EU circular economy goals. Its commitment to reliability and accessible electrification reinforces its position across diverse European markets. Volkswagen Group actively shapes the Europe hybrid cars market by integrating plug-inhybrid variants across its multi-brand portfolio, including Volkswagen, SEAT, and Škoda. The group leverages its modular MQB and MLB platforms to efficiently produce hybrid models such as the Tiguan eHybrid and Octavia iV. In early 20,24 Volkswagen announced enhanced battery capacity for iPlug-in hybrid,s increasinelectric-onlyly range to over 100 kilometers in select models. The company also expanded partnerships with energy providers to offer bundled home charging solutions. Volkswagen’s focus on premium hybrid SUVs and sedans caters to urban professionals and corporate fleets seeking transitional electrification. Its coordinated product and service strategy strengthens its relevance amid evolving EU emissions regulations and consumer expectations. Stellantis plays a pivotal role in the Europe hybrid cars market by deploying its efficient hybrid powertrains across Peugeot, Citroën, Opel, and Fiat brands. The company’s PureTech mild hybrid and plug-in hybrid systems are featured in best-selling models like the Peugeot 308 and Fiat 600. In 2024, Stellantis inaugurated a new hybrid drivetrain production facility in Trnava, Slovakia,ia to support growing European demand. The group also launched an updated version of its EMP2 platform optimized for plug-in hybrid integration with improved weight distribution and energy recovery. Stellantis emphasizes affordability and urban practicality, tailoring hybrid offerings for Southern and Central European consumers. Its broad brand portfolio enables it to address multiple price segments and usage scenarios, solidifying its contribution to Europe’slow-emissionn vehicle transition. Top Strategies Used by the Key Market Participants
Key players in the Europe hybrid cars market prioritize platform modularization to reduce development costs and accelerate time to market for hybrid variants. They expand electric-only range through battery upgrades and energy management software enhancements. Strategic partnerships with charging infrastructure providers improve ownership experience, particularly for plug-in hybrids. Companies align product launches with national incentive schemes and low-emission zone regulations to maximize eligibility and consumer appeal. Additionally, they invest in localized production and battery recycling to comply with EU sustainability mandates and strengthen supply chain resilience. These coordinated actions reinforce competitiveness while navigating the transition toward full electrification without prematurely committing to battery electric vehicles.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Europe hybrid cars market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Degree of Hybridization
Mild-hybrid Full-hybrid Plug-in-hybrid
By Vehicle Type
By Country
UK France Spain Germany Italy Russia Sweden Denmark Switzerland Netherlands Turkey Czech Republic Rest of Europe